Sliding Windows Problem Introduction
Pattern: Linked list or arrays find something among all contigious sub array of some given size.
Problems Discussed
- Inverted Sliding Window [Microsoft OA]
- Other problems
- Maximum Sum subarray of size K
- Smallest subarray with a given sum
- Longest Substring with K Distinct Characters
Inverted Sliding Window [Microsoft OA]
Problem Statement
Suppose \(A[n]\) is an array of integers. Identify a \(r\) length window such that \(A[i] \mid \forall \: i \in [n] \text{ except for } \left[k, k+r \right)\) for some \(k \in [n - r]\) has most number of unique elements.
Approach
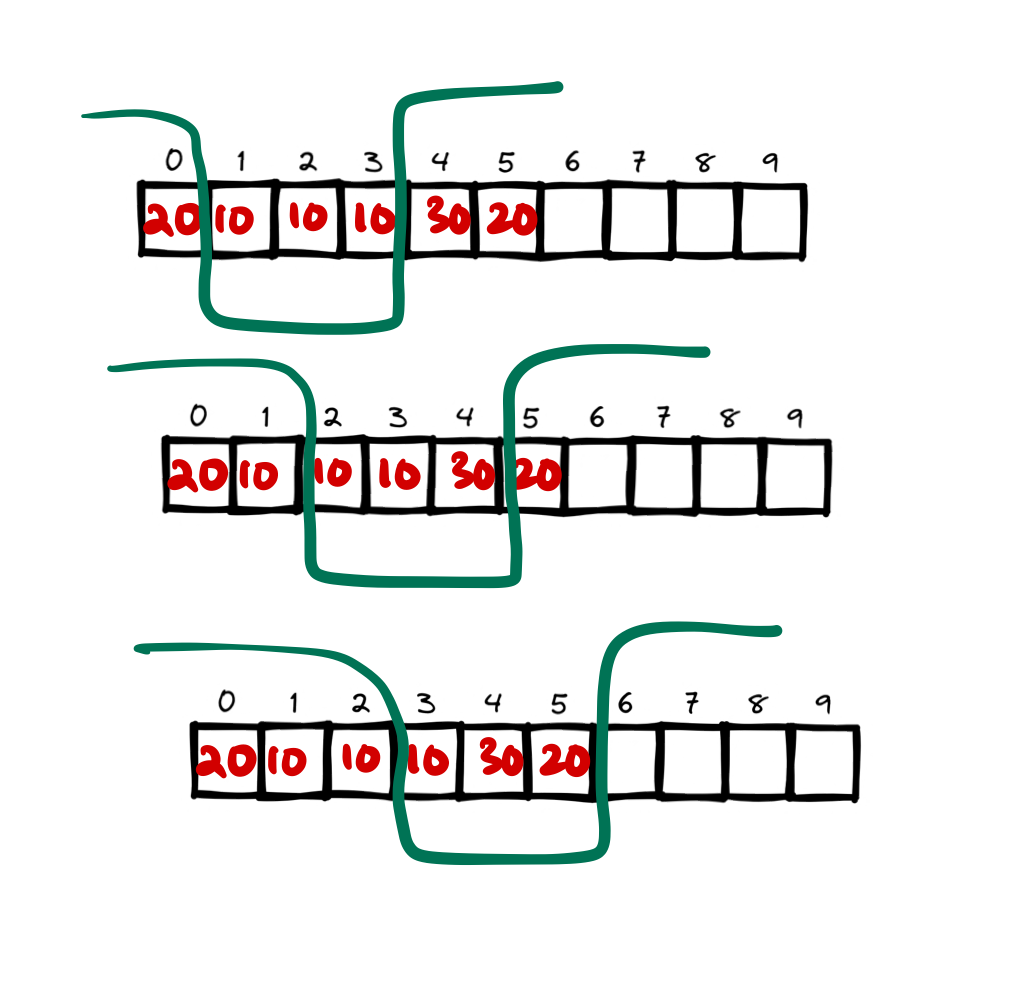
- In first step we calculate the unique elements outside the first window (from \(0 \to r - 1\)),
- Next we slide the window to \((1 \to r)\). In this case the unique element map will add the \(0^{\text{th}}\) element and remove the \(r^{\text{th}}\) element (think of it as the inverted sliding window). We are sliding a window but we are interested outside the window.
- Following is an illustration as to how this window works. Notice the elements outside the bucket rather than the inside. Which is incoming and which is outgoing.
Code
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int testcase;
cin >> testcase;
while (testcase--) {
int n, r;
cin >> n >> r;
if (n == r) {
cout << "0" << endl;
break;
}
int a[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
unordered_map<int, int> freq;
int maximumUniqueWindow = INT_MIN;
// outside first window
int index = 0;
while (index < n) {
if (not(index < r and index >= 0)) {
freq[a[index]]++;
}
index++;
}
maximumUniqueWindow = std::max(maximumUniqueWindow, (int)freq.size());
// for rest of the outside windows
int window_start = 1;
int window_end = r;
int maxWindowStart = 0;
int maxWindowEnd = r - 1;
while (window_end < n) {
// outgoing + incoming from the outside window
int outgoing = a[window_end];
int incoming = a[window_start - 1];
freq[outgoing]--;
if (not freq[outgoing]) {
freq.erase(outgoing);
}
freq[incoming]++;
int currentsize = freq.size();
if (currentsize >= maximumUniqueWindow) {
maximumUniqueWindow = currentsize;
maxWindowStart = window_start;
maxWindowEnd = window_end;
}
window_start++;
window_end++;
}
cout << maximumUniqueWindow << endl;
}
}
Other problems
Given an array, find the average of all contiguous subarrays of size ‘K’ in it.
For a given array: \([1, 3, 2, 6, -1, 4, 1, 8, 2]\) and \(K=5\) means find the average of all the contiguous subarrays of size ‘5’ in the given array.
- For the first 5 numbers (subarray from index 0-4), the average is \((1+3+2+6−1)/5=2.2\)
- The average of next 5 numbers (subarray from index 1-5) is: \((3+2+6-1+4)/5 = 2.8\)
- For the next 5 numbers (subarray from index 2-6), the average is: 2.5 and so on.
Here is the final output containing the averages of all contiguous subarrays of size 5: Output: [2.2, 2.8, 2.4, 3.6, 2.8]
Brute force apprach
A brute-force algorithm will be to calculate the sum of every 5-element contiguous subarray of the given array and divide the sum by ‘5’ to find the average.
def brute_force(array: list[int], K:int) -> list[int]:
# Keep track of the avgs
avgs: list[int] = []
# Start from 0 and go to the next 5 elements and find the average
for i in range(0, len(array)- K+1):
sum: int = 0
for j in range(i, i+K):
sum += array[j]
avg: float = sum / K
avgs.append(avg)
return avgs
mainarray: list[int] = [1, 3, 2, 6, -1, 4, 1, 8, 2]
K: int = 5 # find max of this size for given array
a: list[int] = brute_force(mainarray, K)
from rich.console import Console # For printing purposes
console = Console()
console.print(a)
Problems with this apporach
- Time complexity is huge \(O(N * K)\).
- We are summing up same elements over and over again. For two consecutive subarrays of size 5 we could just add the new incoming elements and subtract the outgoing elements.
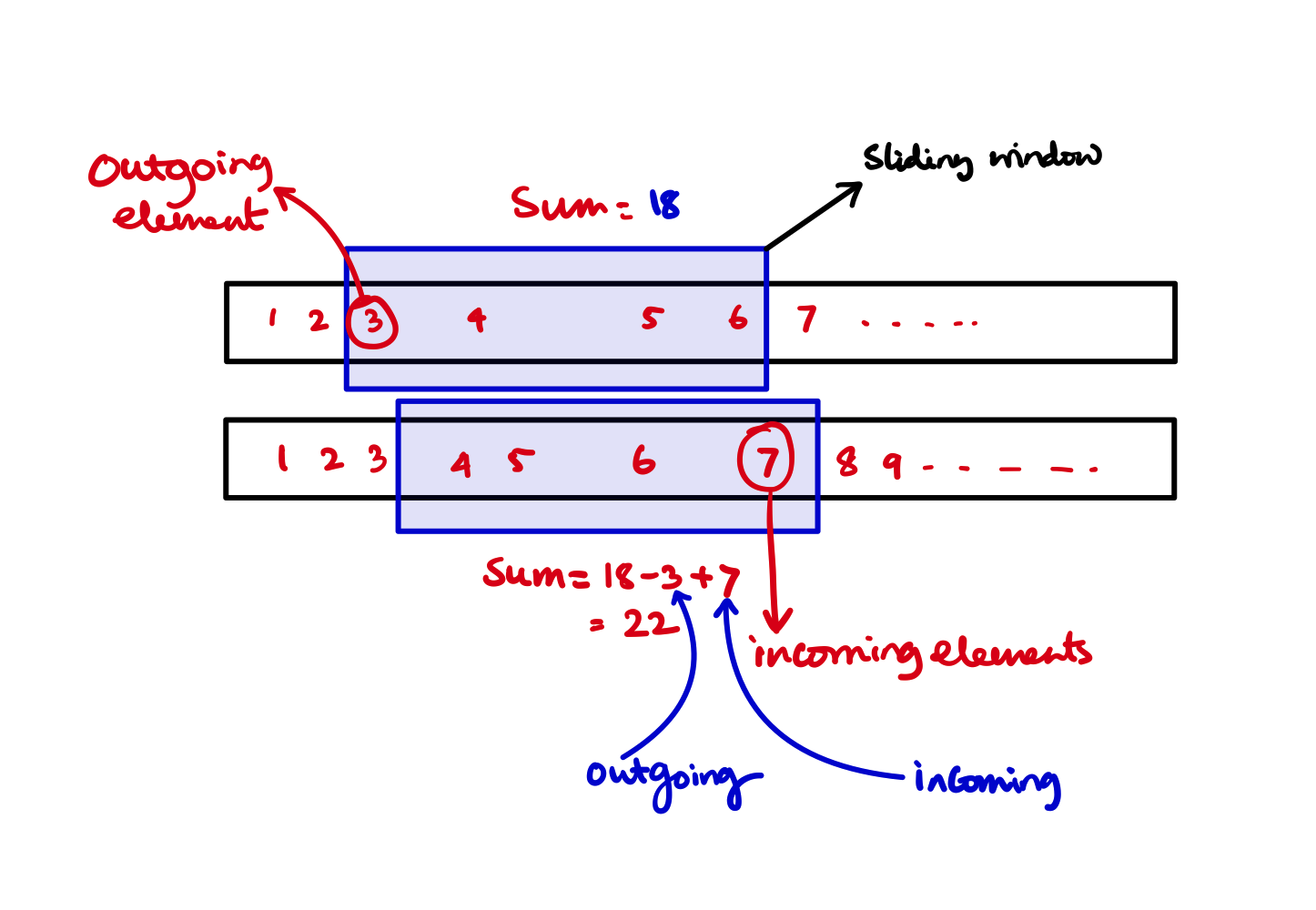
This will reduce the cost to \(O(N)\) with just one time \(O(K)\) summing up program.
def optimized(array: list[int], K: int) -> list[int]:
if K > len(array):
raise IndexError("Error Bro")
# Keep track of all the averages
avgs: list[int] = []
# Start from 0 and go to the next K elements and find the average
sumtillK: int = 0
for i in range(0, K):
sumtillK += array[i]
avgs.append(sumtillK / K)
# If the size of the array is the size of the window then just return
if K == len(array):
return avgs
# From K+1 to Last element for each sliding window add the last
# element and subtract the first element
# Leave the first element and then start from 2nd elemenet
# and slide smoothly
for i in range(1, len(array) - K + 1):
sumtillK = sumtillK - array[i - 1] + array[i + K - 1]
avgs.append(sumtillK / K)
return avgs
Optimized approach with while loop
def optimized_while(array: list[int], K: int) -> list[int]:
avgs: list[int] = []
if K > len(array):
raise IndexError("Error Bro")
sumtillk: int = 0
for i in range(0, K):
sumtillk += array[i]
avgs.append(sumtillk / K)
# Leave the first element and then start from 2nd elemenet
# and slide smoothly
index: int = 1
while index != (len(array) - K + 1):
sumtillk = sumtillk - array[index - 1] + array[index + K - 1]
avgs.append(sumtillk / K)
index += 1
return avgs
b: list[int] = optimized(mainarray, K)
c: list[int] = optimized_while(mainarray, K)
console.print(b)
console.print(c)
Output
Maximum Sum subarray of size K
Problem Statement
Given an array of positive numbers and a positive number ‘k’, find the maximum sum of any contiguous subarray of size ‘k’.
Examples
Input: [2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 2], k=3
Output: 9
Explanation: Subarray with maximum sum is [5, 1, 3].
---
Input: [2, 3, 4, 1, 5], k=2
Output: 7
Explanation: Subarray with maximum sum is [3, 4].
Approach [Naive on back of the envelope approach]
def mss(array: list[int], k:int) -> int:
maximum: int = 0
sumtillK: int = 0
for i in range(0, k):
sumtillK += array[i]
maximum = sumtillK
idx: int = 1
while idx != len(array) - k:
sumtillK = sumtillK - array[idx-1] + array[idx + k -1]
maximum = max(maximum, sumtillK)
idx += 1
return maximum
mainarray: list[int] = [2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 2]
K: int = 3 # find max of this size for given array
a2: list[int] = [2, 3, 4, 1, 5]
k2 = 2
Time complexity
Only one pass of the array so the time complexity is \(O(N)\)
Smallest subarray with a given sum
Problem statement
Given an array of positive numbers and a positive number ‘S’, find the length of the smallest contiguous subarray whose sum is greater than or equal to ‘S’. Return 0, if no such subarray exists.
Examples
Input: [2, 1, 5, 2, 3, 2], S=7
Output: 2
Explanation: The smallest subarray with a sum great than or equal to '7' is [5, 2].
---
Input: [2, 1, 5, 2, 8], S=7
Output: 1
Explanation: The smallest subarray with a sum greater than or equal to '7' is [8].
---
Input: [3, 4, 1, 1, 6], S=8
Output: 3
Explanation: Smallest subarrays with a sum greater than or equal to '8' are [3, 4, 1] or [1, 1, 6].
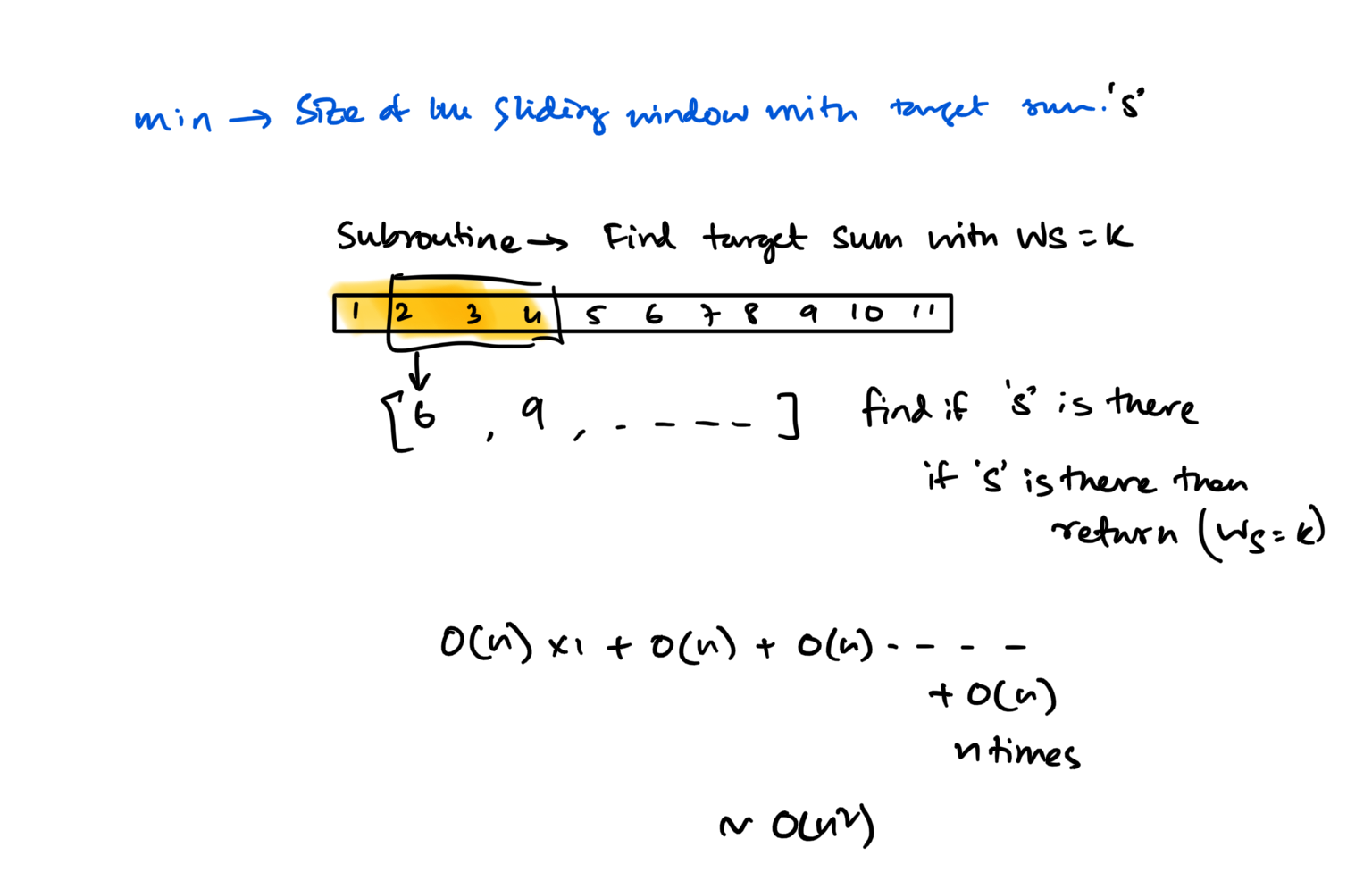
Brute force approach
Key takeway approach
💡 For each size of window find out if the sum is greater or equal to the target?
testcase1: list[int] = [2, 1, 5, 2, 3, 2]
testcase1s: int = 7
testcase2: list[int] = [3, 4, 1, 1, 6]
testcase2s: int = 8
testcase3: list[int] = [2, 1, 5, 2, 8]
testcase3s: int = 7
# Brute force approach
def ssgs(array: list[int], s: int) -> int:
def subroutine(array: list[int], ws: int, target: int):
if ws == 1:
for entires in array:
if entires >= target:
return 1
summation: int = 0
for i in range(0, ws):
summation += array[i]
if summation >= target:
return ws
index = 1
while index < len(array) - ws:
summation = summation - array[index - 1] + array[index + ws - 1]
if summation >= target:
return ws
index += 1
return -1
window_size: int = 1
subroutine_return: int = -1
while window_size < len(array) and subroutine_return == -1:
subroutine_return = subroutine(array, window_size, s)
window_size += 1
return subroutine_return
console.print(ssgs(testcase1, testcase1s),
ssgs(testcase2, testcase2s),
ssgs(testcase3, testcase3s),
ssgs([1, 2, 10, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 17))
Time complexity
\(O(N)\) work for each size of the window and at most \(N\) is the windows size. So \(N*O(N) = O(N^2)\)
Better Optimized approach
- First we add up the elements of the array from start until we get the sum at least the target
- This is the first window size from the array that at least sums upto the target, so we remember the length
- We will remember the length of the window if we find a smaller window than this that sums at least the target.
Coming soon
Room for more understanding
...
Longest Substring with K Distinct Characters
Problem statement
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring in it with no more than K distinct characters.
Input: String="araaci", K=2
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest substring with no more than '2' distinct characters is "araa".
Comments
This comments system is powered by GitHub Discussions